India Develops Pulse Detonation Engine For Cruise, Anti-Tank Missiles
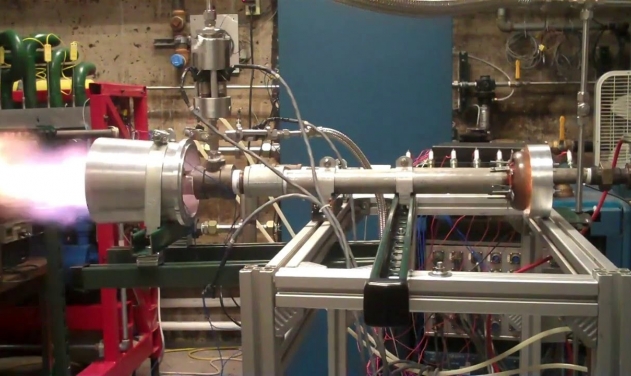
India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has developed a pulse detonation engine which has higher fuel efficiency than the gas turbine ones for cruise, anti-tank missile and unmanned aerial vehicles propulsion.
The pulse detonation engine has higher fuel efficiency than the gas turbine engines of flying systems.
After the basic engine, DRDO's unit Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL) is currently working on air breathing multi-tube, multi-cycle pulse detonation engine, Sputnik news reported Friday quoting an unspecified 'paper.'
“After achieving single shot detonation in a single tube in liquid fuel, TBRL has achieved multi-cycle operation of 8 Hz in single PDS tube.
TBRL is working on air breathing multi-tube multi-cycle pulse detonation engine with an objective to develop an air-breathing Pulse Detonation Engine to generate 2.5 kN of thrust for a duration of 30 minutes, said the DRDO paper.
Pulse detonation system is a mechanically simpler engine in comparison to the gas turbine engine, wherein the combustion wave travels at supersonic speeds relative to the unburnt fuel-oxidizer mixture. Pulse detonation system utilizes repetitive detonations of the fuel-oxidizer mixture to produce thrust.
For flying systems, however, detonation requires a long tube length to accommodate required amount of energy input. TBRL has been working on a system to reduce the length of the engine so that it can be applied in systems like UAVs and other missiles system as well.
“To reduce engine length, suitable devices are employed which reduce the length of the tube required for the transition from deflagration to detonation. A test rig was designed and established for conducting experiments with liquid fuel-air mixtures,” the paper added.













