Leonardo to Study Feasibility of Cloud Computing for Italian Military
Space Cloud enhances military security, global data access, and disaster resilience.
Leonardo has been asked to examine the viability of integrating cloud computing into the operations of the Italian military.
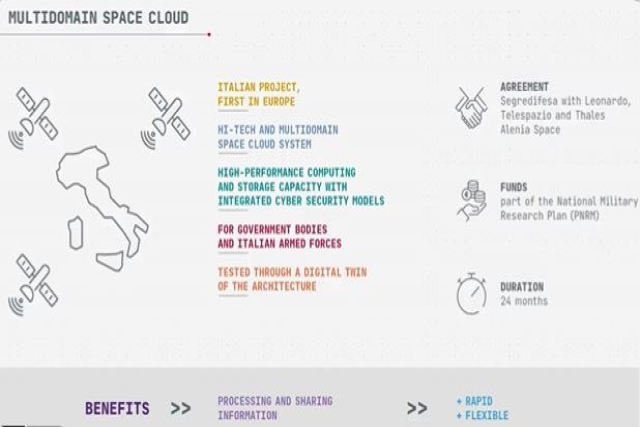
The "Military Space Cloud Architecture" (MILSCA) project, initiated by the Italian Ministry of Defense through the contractual agency Teledife, forms part of the National Military Research Plan (PNRM).
Aiming to create a space-based architecture for high-performance computing and storage, the MILSCA project is a first-of-its-kind endeavor in Europe. It involves a constellation of cyber-secure satellites orbiting the Earth, collectively referred to as the "Military Space Cloud."
The proposed system, designed with integrated cyber security models, promises increased speed and flexibility in processing and sharing information. The Space Cloud will undergo testing by creating a digital twin of the architecture capable of storing over 100 Terabytes of data generated on Earth and in space on each constellation satellite. It boasts a processing power exceeding 250 TFLOPS (250 thousand billion operations per second) at single precision, incorporating advanced algorithms utilizing artificial intelligence, machine learning techniques, and extensive data analysis. The satellites can also autonomously communicate and exchange data with each other.
This cyber-secure supercomputer and archive system in space aims to provide users with access to strategic data, including communication, earth observation, and navigation data, regardless of location or time. Furthermore, the Space Cloud is expected to reduce data processing times significantly, providing real-time information for multi-domain and multi-national operations. This approach will free up transmission networks for other connections by transferring only the essential information to Earth.
Simone Ungaro, Chief Innovation Officer at Leonardo, highlighted the significance of the project, stating, "In a multi-domain scenario, management, security, and rapid exchange of an ever-increasing amount of data, much of which is tactical, become strategic elements for the country's defense." Ungaro emphasized that the Space Cloud project positions Leonardo at the forefront of technological innovation, demonstrating the feasibility and benefits of this unique architecture.
The MILSCA study, spanning 24 months, involves defining the architecture in the first phase and developing a digital twin of the satellite with the High-Performance Computing (HPC) and multi-constellation satellite terminal demonstrator in the second phase. The study will leverage Leonardo's supercomputer, davinci-1, known for its significant computing power and performance in the aerospace and defense sectors.
The project is a collaborative effort with joint ventures Telespazio and Thales Alenia Space, and its success could lead to the deployment of a demonstrative constellation of satellites in orbit. The Space Cloud for Defense project also lays the groundwork for potential future applications, including support for civil Earth observation programs and space exploration missions to the Moon and Mars, benefitting from an in-orbit cloud computing architecture for faster data download and processing.









