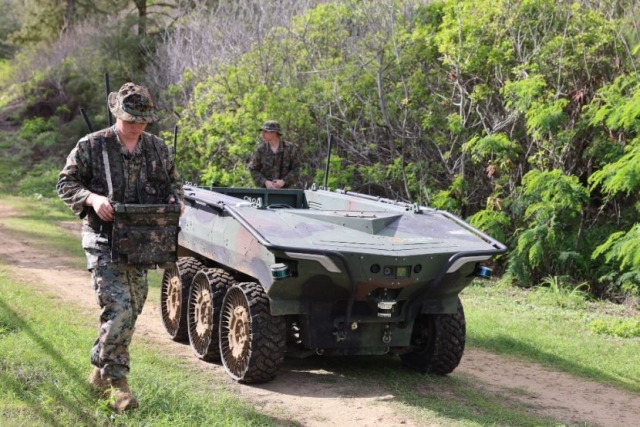
70 Percent of DARPA Projects Utilize AI, Machine Learning, and Autonomy
DARPA's key aim is to create trustworthy AI for the DoD, especially for life-and-death decisions for warfighters: DARPA official

A top U.S. defense official announced today that approximately 70% of projects within the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) are leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, and autonomy in various capacities.
Matt Turek, the deputy director of DARPA's Information Innovation Office, emphasized the agency's commitment to developing trustworthy AI for the Defense Department, particularly in scenarios where AI recommendations could influence life-or-death decisions for warfighters.
Speaking at a Center for Strategic and International Studies event, Turek highlighted the dual imperative behind DARPA's AI development efforts. Firstly, the agency aims to mitigate the risk of adversaries achieving "strategic surprise" through unexpected technological breakthroughs. Secondly, DARPA endeavors to foster its own strategic advantages through innovation.
To achieve these goals, Turek outlined DARPA's strategy of sourcing transformative capabilities and ideas from both industry and academia. He underscored the importance of initiatives like challenges, where private sector teams compete for prizes, often worth millions of dollars, by presenting innovative solutions.
One such initiative highlighted by Turek is the DARPA Artificial Intelligence Cyber Challenge, which harnesses generative AI technologies, such as large language models, to automatically identify and address vulnerabilities in critical open-source software
Large language models, Turek explained, have versatile applications including secure computer coding, decision-making, speech recognition, and predictive analytics.
DARPA has partnered with leading large language model providers such as Google, Microsoft, OpenAI, and Anthropic to advance this technology.
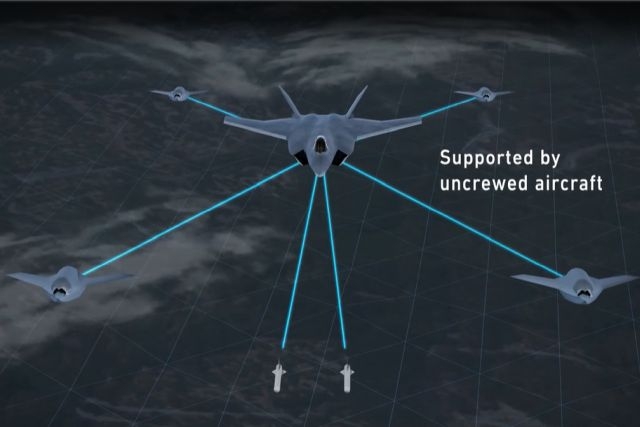
Turek also shared examples of DARPA's collaboration with the Air Force, particularly in testing autonomy and AI integration with F-16 fighter jets.
The DARPA official identified four key areas of AI research involving partnerships with industry and academia: Proficient artificial intelligence; Confidence in the information domain, encompassing tools to detect manipulated media; Secure and resilient systems; and Defensive and offensive cyber tools.