Gaza Hospital Explosion Brings Focus on Joint Direct Attack Munition
The Al-Ahli Gaza hospital attack whodunnit

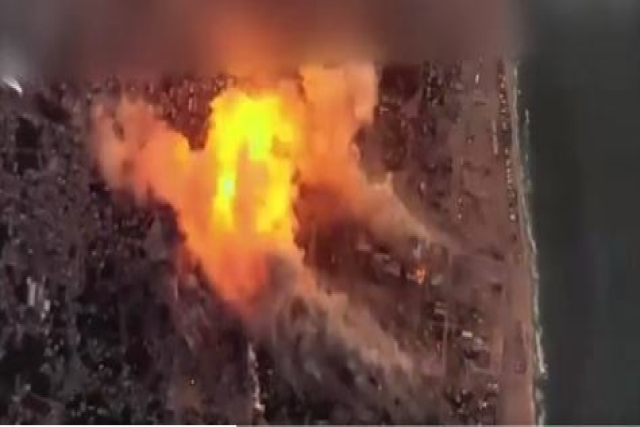
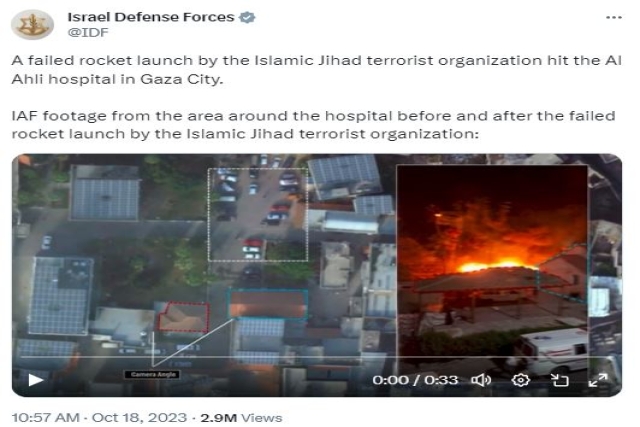
Israel’s alleged use of a bomb equipped with a Joint Direct Attack Munition (JDAM) kit to hit the 140-year-old Al-Ahli hospital in Gaza killing 500 people has raised curiosity on what a JDAM really is.
Israel has denied it bombed the hospital claiming that the extensive damage was caused by a misfired Hamas rocket.
The JDAM is a guidance kit designed to convert unguided bombs into precision-guided munitions. Developed by Boeing, the JDAM has become a staple in the arsenals of many military forces around the world. What sets JDAM apart is its ability to navigate towards its target with GPS guidance, enabling its payload to hit with pinpoint accuracy.
Precision Bombing Capability of JDAMs:
JDAMs are a preferred choice for military forces seeking to minimize collateral damage. They can hit a target with a 1.7-meter circular error of probability (CEP), according to Boeing.
These munitions offer the following benefits:
JDAM kits use GPS to guide bombs to their intended targets, ensuring a high degree of accuracy. This minimizes the risk of stray bombs causing unintended harm.
JDAM kits can be integrated into a wide range of bomb types, providing flexibility to match the desired explosive power and purpose of the mission.
Watch video: JDAM Bomb, not Hamas Rocket, Caused Gaza Hospital Blast that Killed Over 500 Palestinians

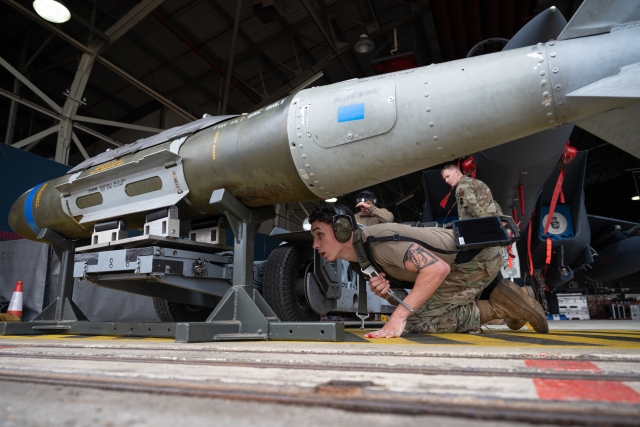
JDAM Laser Guidance:
While JDAMs primarily rely on GPS guidance, laser guidance systems have been integrated to enhance precision further. These laser JDAMs are particularly useful in situations where GPS signals may be jammed or disrupted.
Different Types of JDAM Kit/Bombs:
The versatility of JDAM technology lies in the availability of various bomb types that can be fitted with JDAM kits:
Mk-82 JDAM: The Mk-82 is a 500-pound class bomb often used for precision strikes. The JDAM kit allows it to achieve pinpoint accuracy.
Mk-84 JDAM: A 2,000-pound class bomb, the Mk-84 JDAM is suitable for larger targets that require a significant explosive payload.
BLU-109 JDAM: The BLU-109 is a penetrating warhead designed to destroy hardened or deeply buried targets. JDAM guidance enhances its accuracy, making it even more effective.
Laser JDAMs: As mentioned earlier, laser JDAMs utilize laser guidance for pinpoint accuracy, complementing GPS guidance in situations where GPS signals might be unreliable.
Extended Range JDAM (ER JDAM): These kits extend the range of JDAM munitions, enhancing the strike capability by enabling bombs to hit targets from greater distances.
When JDAM carries an explosive warhead, an explosion occurs upon impact with the target. The size and type of explosion depend on the specific JDAM kit and bomb configuration used. JDAMs can be equipped with various warhead types, including high-explosive, bunker-busting, or penetrator warheads, depending on the intended target.
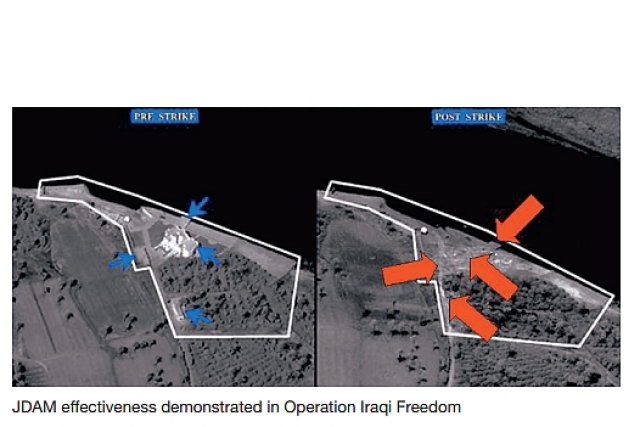
In a world where minimizing collateral damage and achieving surgical precision in strikes is paramount, JDAM technology represents a significant advancement in the field of military weaponry.
Al-Ahli attack whodunnit: Why are some experts suggesting Israel could be the culprit behind the Al-Ahli hospital incident?
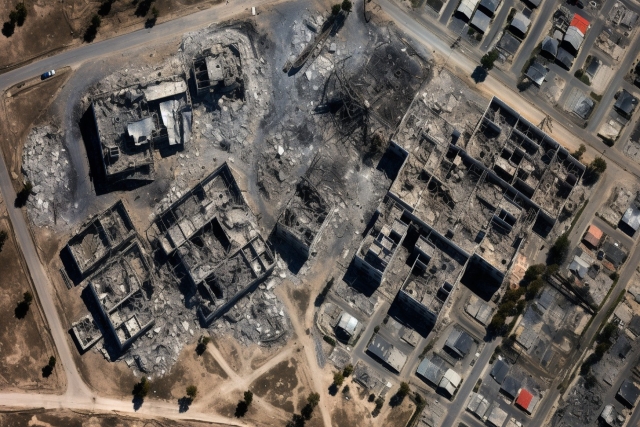
Images circulated on social media indicate that the Al-Ahli hospital was the primary target of the explosion, with minimal damage to surrounding structures. The claim is made that Palestinian Hamas lacks precision strike capabilities, suggesting that the responsibility for this incident may not lie with them. The BBC's satellite imagery supports this assertion, showing limited damage to the hospital's vicinity, including scorch marks and burnt-out vehicles.
Another critical aspect under scrutiny is the crater left by the explosion. The Israeli Defense Force (IDF) points to the presence of a single small crater and the absence of significant damage to nearby buildings as evidence that their weaponry may not be responsible for the explosion.
However, the characteristics of the crater can be influenced by factors such as the specific JDAM warhead, the target's composition, and the depth of penetration. JDAM munitions vary in their crater-forming potential, ranging from no visible crater in the case of penetrating warheads to variable craters with high-explosive warheads, and some JDAMs can even be programmed to burst above the target's surface, leaving no significant crater. The precise circumstances and JDAM configuration are critical in determining the outcome upon impact.